A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Introduction
Home solar systems offer energy independence, substantial cost savings, and environmental benefits, making them a compelling option for those new to renewable energy. However, understanding how these systems work, their benefits, and the installation process can be daunting for beginners.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about solar home systems—from the basics of solar energy to the different types of systems and key factors to consider before installation. This guide will help you decide if a solar home system is right for you.
What Is a Home Solar System?
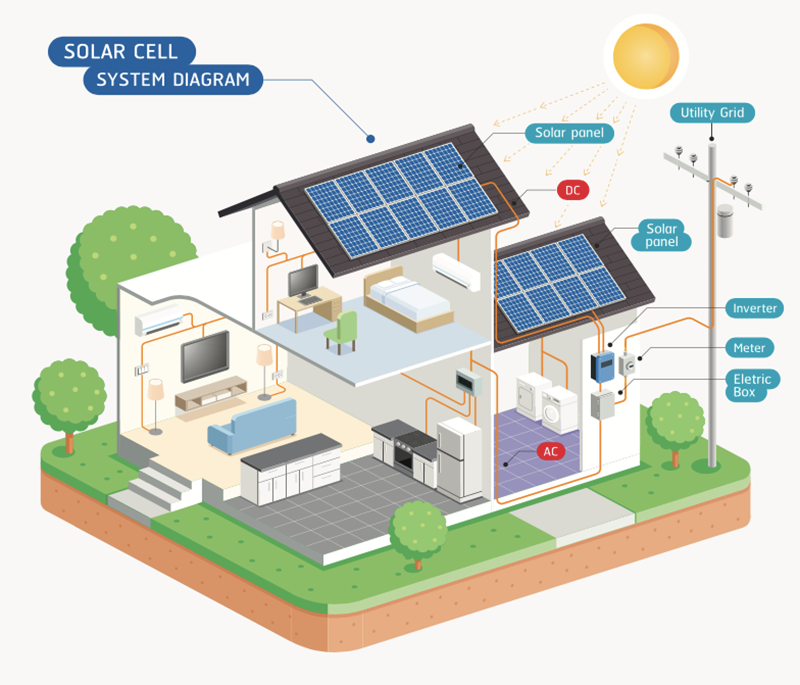
A home solar system, also known as residential solar, harnesses sunlight and converts it into usable electricity for your home. These systems typically include:
- Solar Panels: These panels contain photovoltaic (PV) cells that capture sunlight and transform it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter: The inverter converts DC electricity from the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which powers home appliances.
- Battery Storage (optional): Batteries store excess energy for use during nighttime or power outages, giving you more control over your energy usage.
The system connects to your home’s power grid, allowing you to draw energy from the grid when necessary or potentially sell excess energy back through a process called net metering.
Benefits of Installing a Solar Home System
1. Energy Cost Savings
By generating your own power, you can reduce reliance on traditional energy sources, leading to lower monthly electricity bills. Over time, these savings can offset the initial investment in the solar system, resulting in significant financial benefits.
2. Increased Home Value
Homes equipped with solar panels often sell at higher prices than those without. Buyers appreciate the environmental and financial perks, which can make your property more attractive on the real estate market.
3. Energy Independence
Solar energy enables homeowners to produce their own electricity, reducing dependence on local utility providers. Systems with battery backup also provide a safeguard during grid outages, ensuring you have electricity when you need it most.
4. Environmentally Friendly
Solar energy is renewable, which means using it reduces your carbon footprint. A typical residential solar system can offset tons of carbon dioxide emissions annually, helping you contribute to a cleaner, greener planet.
5. Low Maintenance Requirements
Once installed, solar panels require minimal maintenance. Many panels come with warranties of 20–25 years, and occasional cleaning is usually sufficient to keep them operating efficiently.
Types of Solar Home Systems
Choosing the right type of solar system depends on your energy needs, location, and preferences. Here are the three primary types:
1. Grid-Tied Solar Systems
Grid-tied systems are connected to the local electricity grid, allowing homeowners to draw from the grid during low-sunlight periods or when energy demand exceeds solar production. In many areas, net metering enables homeowners to earn credits for excess electricity fed back into the grid, reducing energy costs.
2. Off-Grid Solar Systems
An off-grid system operates independently from the local grid. These systems are suitable for remote areas and typically require larger batteries to store energy. While they offer complete energy independence, they may have higher initial costs due to the need for sufficient battery capacity.
3. Hybrid Solar Systems
Hybrid systems combine features of both grid-tied and off-grid systems. They are connected to the grid but include batteries for backup storage. This setup provides flexibility, as homeowners can use stored power during outages or peak demand times, making it ideal for those seeking both reliability and cost savings.
Key Considerations Before Installing a Solar System
Installing a solar system involves several considerations that affect the cost, efficiency, and overall experience. Here are some important factors:
1. Location and Sunlight Exposure
Your home’s location, roof orientation, and shading all influence solar panel efficiency. Ideally, your panels should receive unobstructed sunlight throughout the day for maximum energy production.
2. Energy Requirements
Determine your household’s daily and monthly energy needs to decide how large your solar system should be. This will help you select the right number and size of solar panels.
3. Budget
While solar panel prices have dropped significantly, installation costs vary. Contact multiple solar providers to get quotes that include equipment and installation to find the best value for your investment.
4. Rebates and Incentives
The U.S. federal government offers a solar tax credit (currently 30% of installation costs) to reduce the financial burden of going solar. Some states and utilities also offer additional incentives, so be sure to research local programs.
5. System Maintenance
Solar panels generally require little maintenance, but periodic cleaning and professional inspections can help ensure they operate at peak efficiency. Most installers offer warranty packages, covering repairs and maintenance for a specified period.
How to Install a Solar Home System: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Site Assessment and Design
A solar installation company will assess your home’s structure and sunlight exposure to design a custom system suited to your needs. This step involves evaluating roof space, angles, and structural integrity.
2. Permitting and Paperwork
Most solar installations require local permits and regulatory approvals. Your installer usually handles this process, ensuring your system complies with building codes and zoning laws.
3. Panel Mounting
The mounting system attaches the panels securely to your roof, allowing them to capture sunlight efficiently. Installers may drill into your roof but will seal and weatherproof any openings to prevent leaks.
4. Electrical Wiring and Inverter Setup
Next, installers connect the panels to an inverter, which converts DC electricity into AC for your household’s use. They also link the system to your home’s electrical panel, enabling seamless integration with existing power sources.
5. Testing and Activation
After installation, the system undergoes thorough testing to verify proper operation. Once approved by local authorities, your solar system is ready to start generating clean energy for your home.
Frequently Asked Questions About Solar Home Systems
Q: Can I go completely off-grid with a solar home system?
Yes, but this setup requires a robust battery system to store enough power for nighttime use and cloudy days. Off-grid systems are ideal for remote locations but often cost more due to the battery capacity needed.
Q: How many solar panels do I need for my home?
The number of panels depends on your home’s energy consumption, panel efficiency, and available roof space. On average, a 2,000 sq. ft. home might need 24–32 panels to meet its energy needs.
Q: What happens on cloudy or rainy days?
Solar panels still generate electricity on cloudy days, though at reduced efficiency. Hybrid or off-grid systems with battery backup ensure you have power regardless of the weather.
Conclusion
Solar home systems present a powerful way to reduce electricity costs, achieve energy independence, and minimize environmental impact. By understanding the different system types, assessing your energy needs, and exploring available incentives, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial and environmental goals. Investing in solar is a commitment to sustainable living and a cleaner, greener future.